
Figure 2 from Culture conditions for primary human limbal epithelial cells. Semantic Scholar
1.1.4 Corneal stem cells. The limbus of the cornea is located at the junction of the cornea, conjunctiva, and sclera. It differs from conjunctiva as it does not have goblet cells and is about 1 mm wide; the epithelial cell layer contains over 10 layers and is irregularly arranged. Moreover, the cells are rather small and cylindrical and possess.

Schematic of an eye showing a normal limbus (red), partial limbal stem... Download Scientific
The sclera-corneal junction is called the limbus. Here, the deep surface of the suprachoroid lamina is covered by the scleral endothelium, a simple squamous epithelium. The limbus is the location of corneal stem cells. The sclera is nearly avascular, although it does have some visible blood vessels that pierce the surface to reach the retina below.
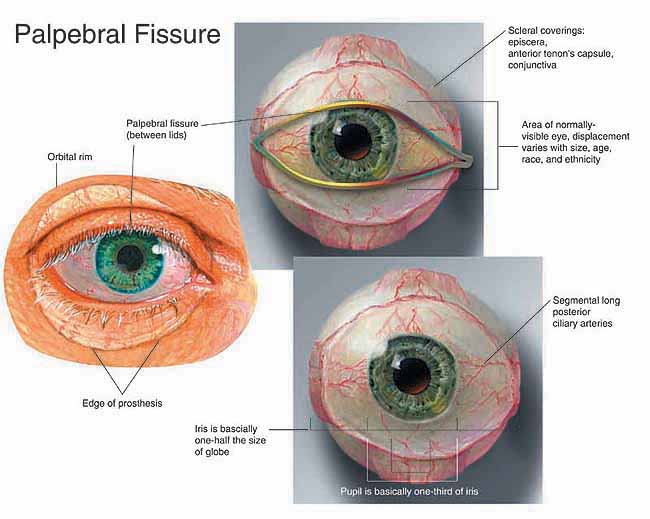
JBC 31.2 Depicting the Anterior Eye in Two and Three Dimensions, Part Two Iris, Limbus and Sclera
The limbus is the transition zone preventing the opaque epithelium from invading the clear cornea. Click image to enlarge. Cells and Components LSCs are most concentrated in areas of the limbus called the palisades of Vogt. To a lesser degree, they are also located in limbal epithelial crypts and the limbal epithelial pit.

THE LIMBUS Eye anatomy, Anatomy, Optometry
Your cornea, which is the membrane that covers your eye like a lens, and the sclera, the white part of your eye, meet at ridges on your eye called the "corneal limbus." This border is.
Eyeball Anatomy Eyeball and Corneal Disease Pathology Teaching Eye Disease Model
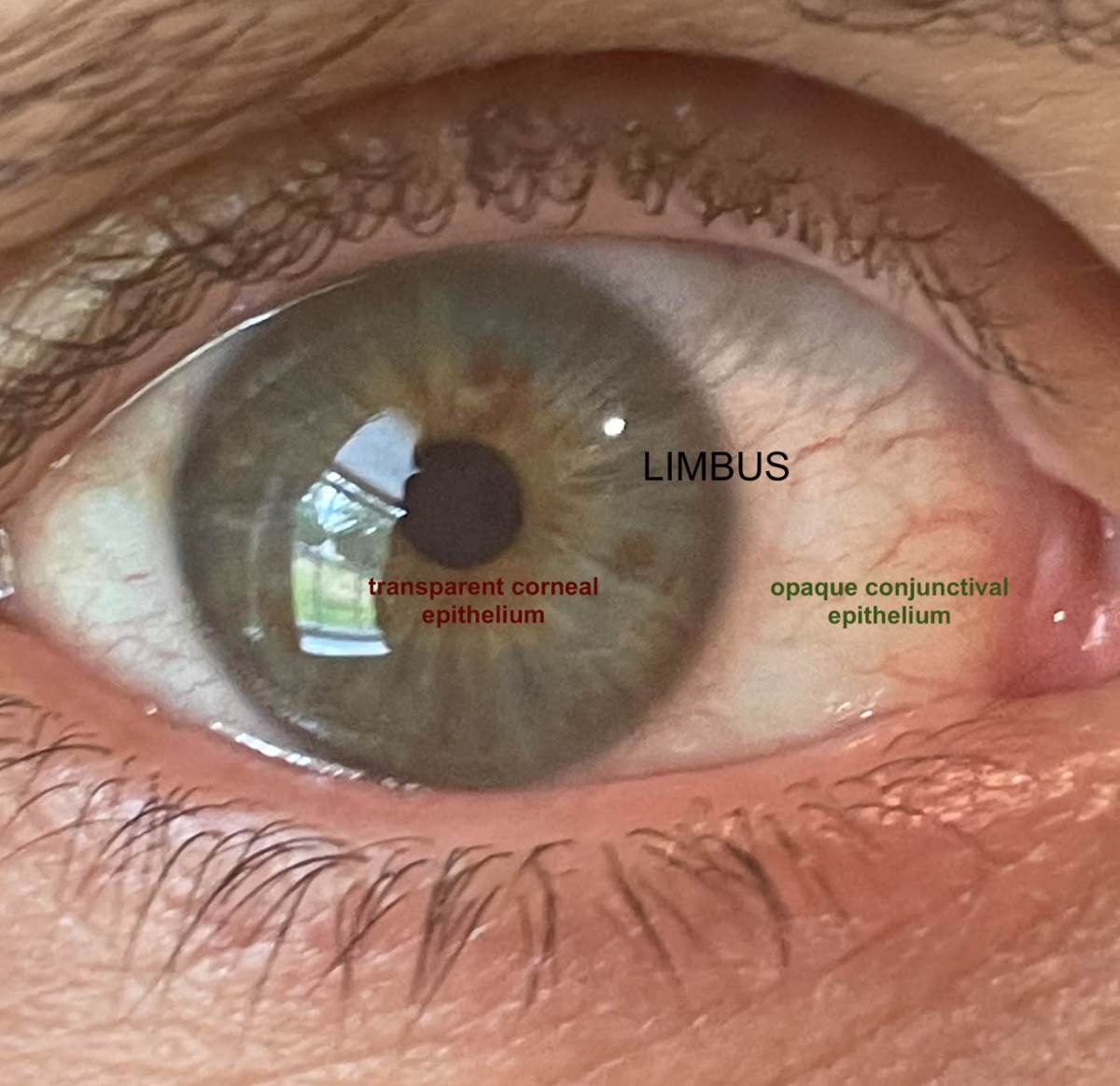
The limbus is the border between the clear part of the eye (cornea) and the white part of the eye (sclera). If you look into the mirror at the colored part of your eye, the limbus is the transparent ring that forms a border around it.

Anatomy Of The Eye Limbus The Anatomy Stories
Part I: Anatomy Chapter 2: The Eye Limbus The transition zone between the peripheral cornea and the anterior sclera, known as the limbus (also called corneoscleraljunction or corneal limbus ), is defined differently by anatomists, pathologists, and clinicians.

9 The human eye, with labelled pupil, sclera, iris and limbus. Download Scientific Diagram
The limbus is widest in superior and inferior cornea. Cornea is convex and aspheric. The anterior curvature is 7.8 mm and posterior curvature is about 6.5 mm. Cornea contributes to about 40-44 D of refractive power and accounts for approximately 70% of total refraction. The refractive index of cornea is 1.376.

Morphological and histological architecture of the human limbus.... Download Scientific Diagram
The limbus of the eye marks the transition between the cornea and sclera. It is a ring-shaped area that starts off transparent by the cornea and becomes opaque near the sclera. The limbus is typically around 1-2mm wide and helps keep the cornea healthy and clear. is the clear covering at the center of the eye.

Anatomy of the Extraocular Muscles Ento Key
LSCD can be caused by any process that diminishes the number of stem cells or disturbs the stem cell environment. 1 With the exception of some congenital conditions and neoplasia, each of the disorders listed in the table, next page, is associated with significant ocular surface inflammation. Diagnosis Presentation.

Cornea Gene Vision
A limbal ring is a dark ring around the iris of the eye, where the sclera meets the cornea. [1] It is a dark-colored manifestation of the corneal limbus resulting from optical properties of the region. [2] The appearance and visibility of the limbal ring can be negatively affected by a variety of medical conditions concerning the peripheral.
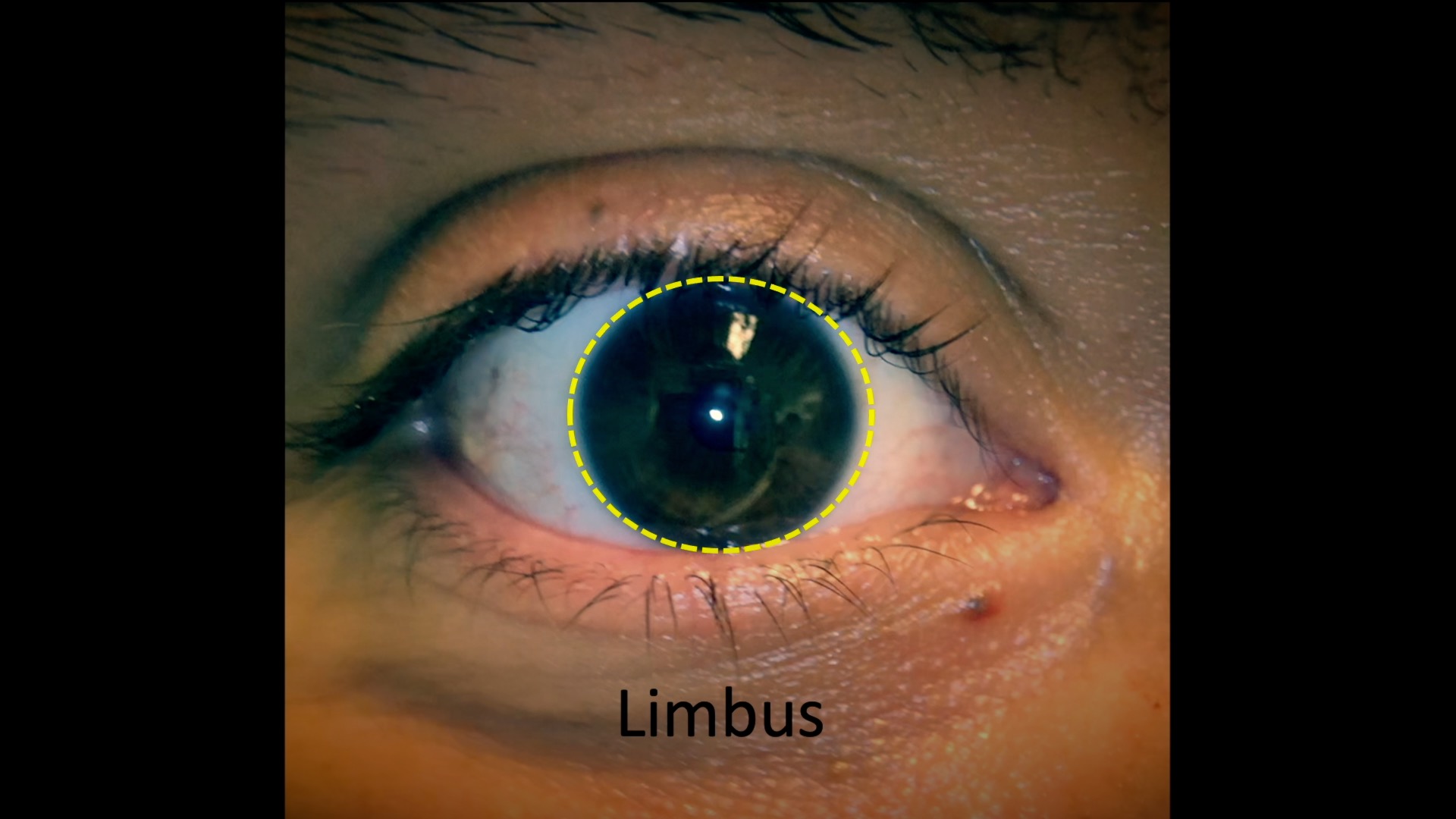
Limbal Landmarks
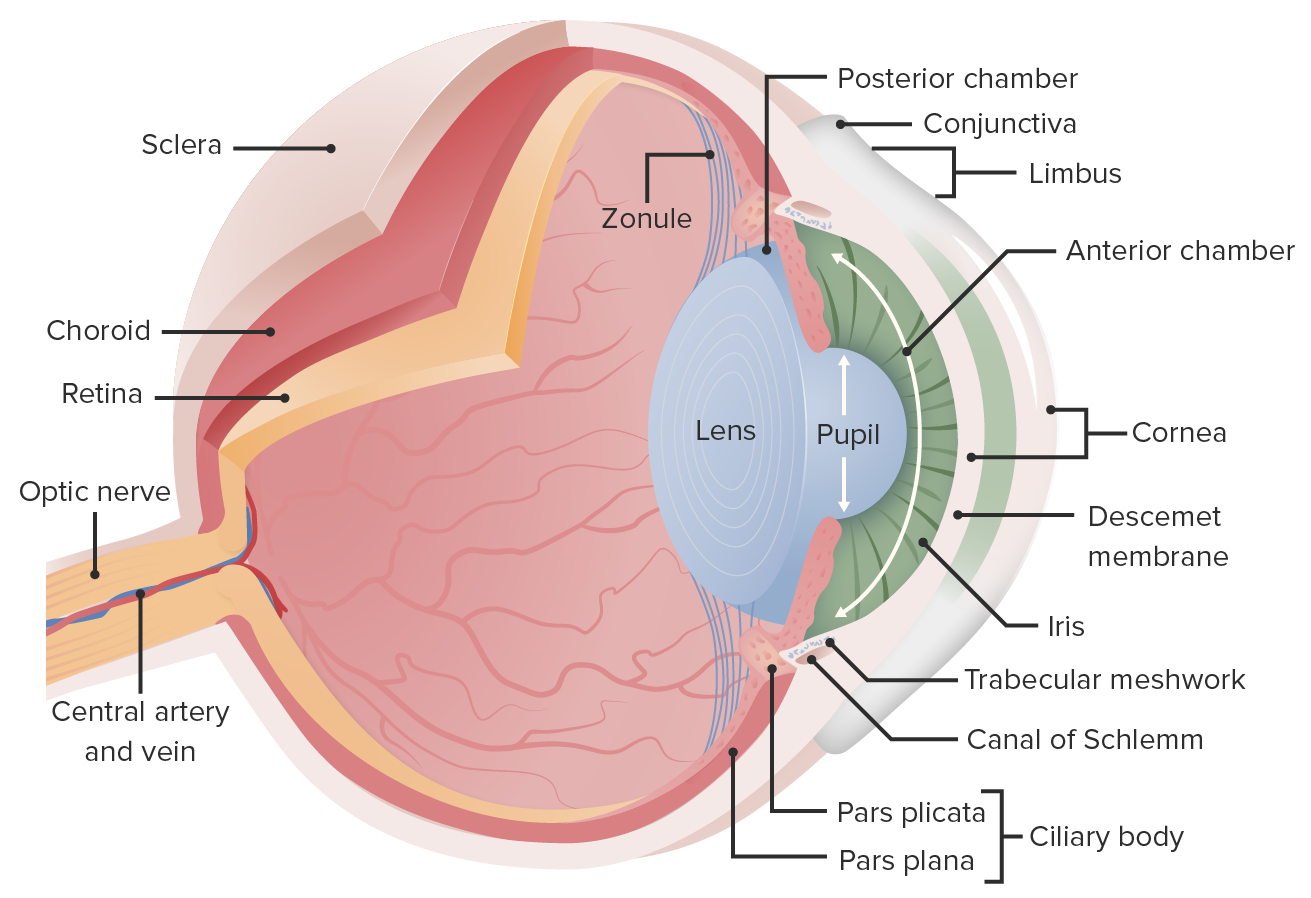
The outer coats of the eye are the cornea and sclera; their juncture is the limbus ( Fig 2.1 ). The interior of the eye is divided into the anterior and posterior segments. The anterior segment includes the cornea, iris, ciliary body and lens as well as the spaces of the anterior and posterior chambers filled with aqueous humor.

Pin on study help
Corneal involvement is the result of the spread of abnormal epithelium from the adjacent limbus. The abnormal squamous cells often have a translucent, grayish, frosted appearance. In addition, the corneal lesions often take on a characteristic fimbriated or pseudopodia configuration. [2]

(A) Location of the limbus showing the superior, inferior, nasal, and... Download Scientific
eye anatomy In human eye: General description.areas join is called the limbus. Thus, on looking directly into the eye from in front one sees the white sclera surrounding the cornea; because the latter is transparent one sees, instead of the cornea, a ring of tissue lying within the eye, the iris. The iris is the structure…
Anterior Segment Eye Examination OSCE Guide Geeky Medics
The corneoscleral limbus is a unique and critical ocular structure responsible for barrier protection, corneal regeneration and wound repair. These functions are pivotal in maintaining corneal transparency and ocular surface integrity.

Recent discovery could save peoples' sight
Limbal function is a key determinant of corneal epithelial integrity. Lineage tracing studies in mice have highlighted that the centripetal movement of epithelial progenitors from the limbus drives both the steady-state maintenance of the corneal epithelium and its regeneration following injury. It.
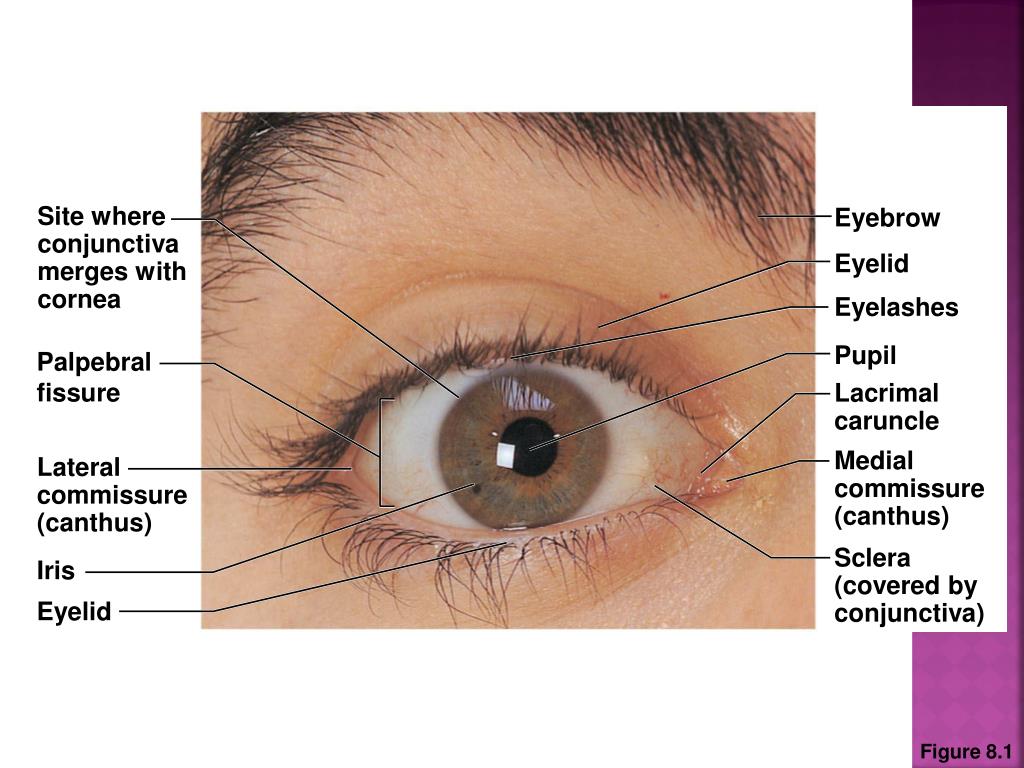
PPT Anatomy of the Eye & the 12 cranial nerves PowerPoint Presentation ID2393441
6.1 Corneal Layers. The cornea is composed of five layers, epithelial, bowman's, stroma, descemet, and endothelial layer (Fig. 6.1 ). Cross-section from the center of the cornea showing the main layers along with the thickness of each layer. Epithelium (50 μm): There are five layers centrally, and ten at the limbus.